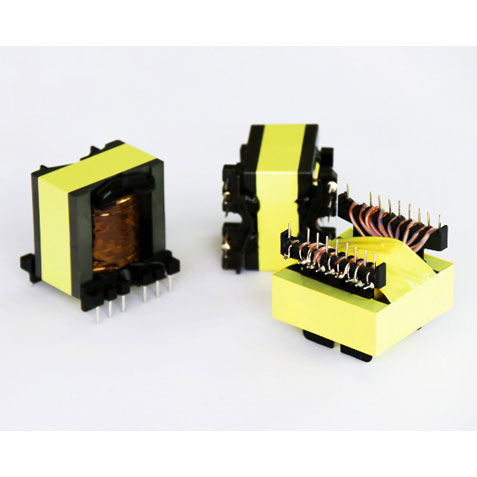
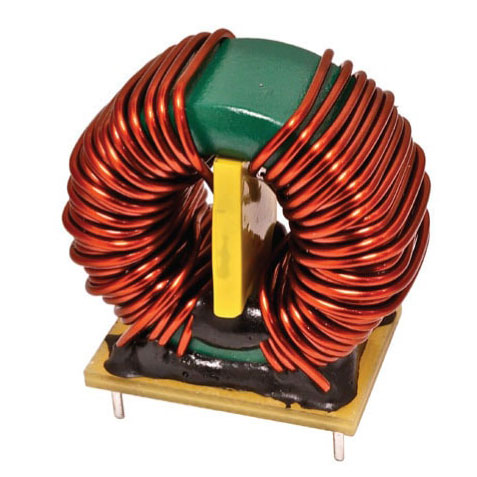
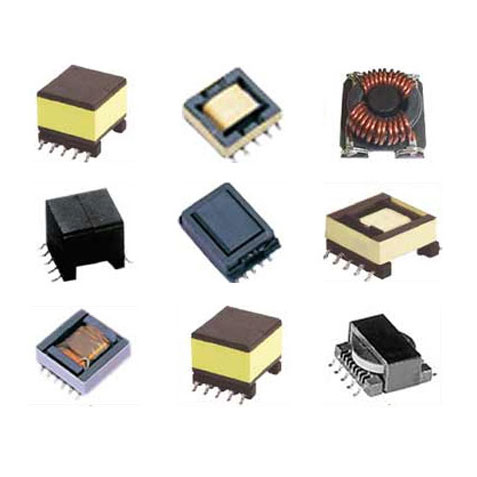
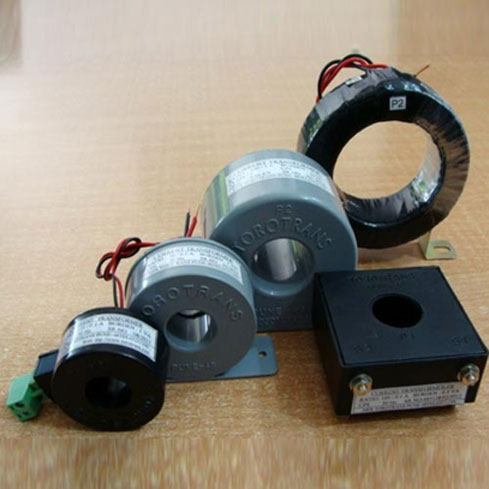
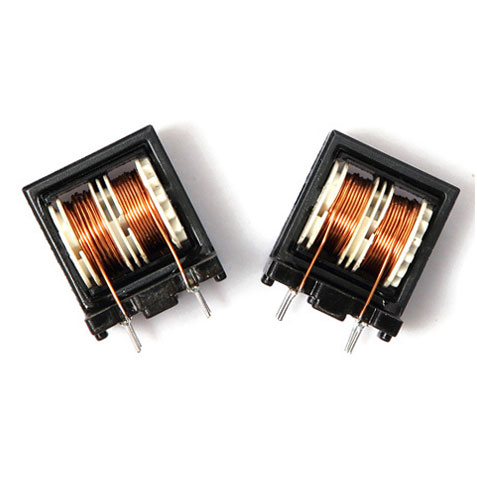
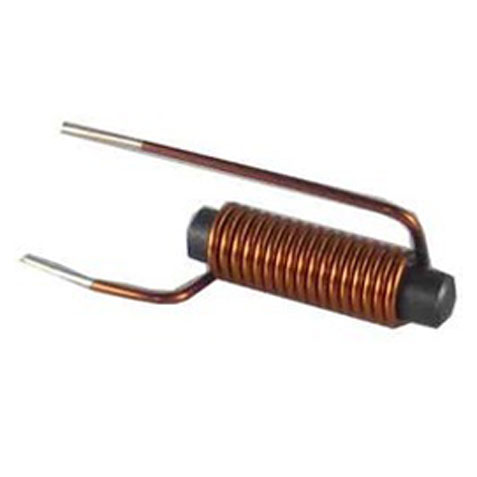
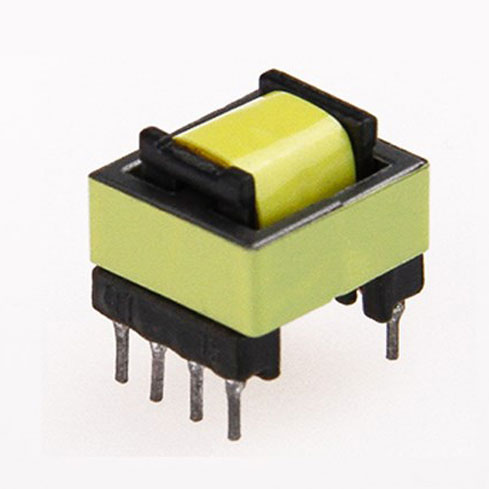
HF Transformer

HF Transformer
Other Fittings Components
High-Frequency Transformers: Precision and Efficiency in Power Conversion
High-Frequency Transformers (HFTs) are essential components in modern electronic systems, facilitating efficient power conversion and signal isolation. Operating at elevated frequencies, these transformers are integral to applications such as switch-mode power supplies (SMPS), radio-frequency (RF) circuits, and communication systems.
Understanding High-Frequency Transformers
High-Frequency Transformers are designed to operate effectively at frequencies typically ranging from 20 kHz to several MHz. Their primary function is to transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction, while providing electrical isolation and impedance matching. This capability is crucial in applications where size, weight, and efficiency are critical factors.
Key Features
- Compact Design: Optimized for space-constrained environments, HFTs are engineered to be compact without compromising performance.
- High Efficiency: Designed to minimize energy losses, ensuring efficient power conversion and reduced heat generation.
- Electrical Isolation: Provides galvanic isolation between primary and secondary windings, enhancing safety and protecting sensitive components.
- Wide Frequency Response: Capable of operating effectively across a broad frequency range, making them versatile for various applications.
Applications
High-Frequency Transformers are utilized in numerous applications, including:
- Switch-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS): Essential for voltage regulation and power conversion in SMPS systems.
- Communication Systems: Used in RF circuits for signal modulation and demodulation.
- Medical Equipment: Provides isolation and power conversion in medical devices.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Facilitates efficient power conversion in solar and wind energy applications.
TechnoFlick Electronics: Your Partner in High-Frequency Transformer Solutions
At TechnoFlick Electronics, we specialize in the design and manufacture of high-quality High-Frequency Transformers tailored to meet the specific needs of our clients. Our commitment to innovation and quality ensures that each transformer is crafted to deliver optimal performance and reliability.
Our Approach
1. Consultation and Design: We collaborate closely with clients to understand their unique requirements, providing customized design solutions.
2. Advanced Manufacturing: Utilizing state-of-the-art technology and materials, we produce transformers that meet stringent quality standards.
3. Rigorous Testing: Each transformer undergoes comprehensive testing to ensure it performs reliably under specified conditions.
4. Customer Support: We offer ongoing support and guidance to ensure our products continue to meet client expectations throughout their lifecycle.
Why Choose TechnoFlick Electronics?
- Expertise: A team of experienced engineers dedicated to delivering innovative solutions.
- Customization: Tailored products to meet unique application requirements.
- Customer Satisfaction: A commitment to exceeding client expectations through quality and service.
For more information on our High-Frequency Transformers and other products, please visit our website or contact our sales team.

1 Years Ragular
Ask Price
| Price: | as per client |
|---|---|
| Unit: | 0 |
| Type: | Products |
Suggested Similar HF Transformer
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium
Ask Price
We are one of the foremost manufacturers of premium